5
5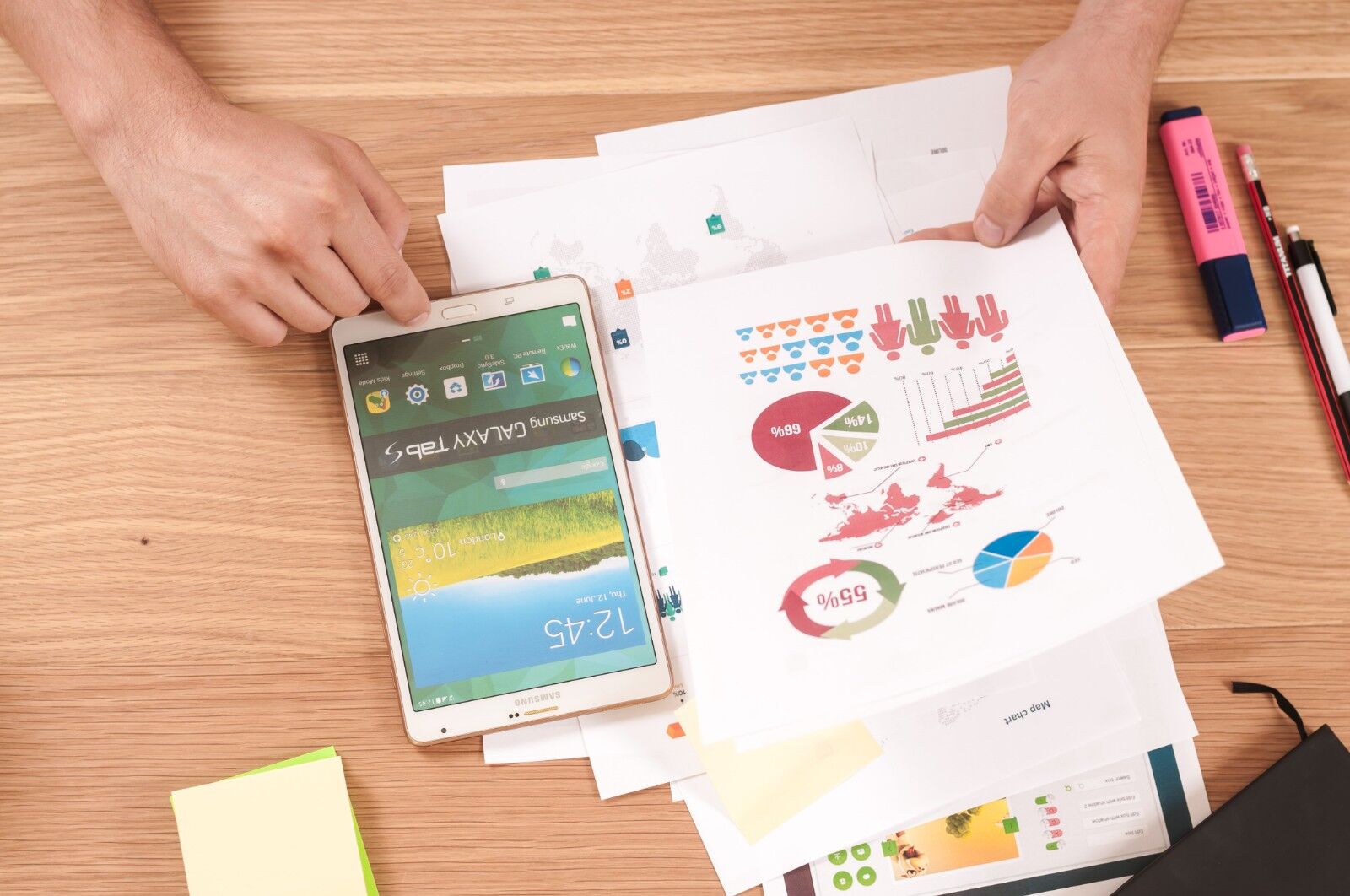
Trade data is a vital tool for companies across industries, offering valuable insights into market trends, supply chain dynamics, and consumer demand. By leveraging different types of trade data, businesses can develop more targeted strategies and enhance their market competitiveness. Below, we explore several common types of trade data and how they can be effectively used in business analysis and decision-making.
Import and export data is one of the most widely used types of trade data. It reflects the movement of goods across international borders, including details such as product quantity, pricing, country of origin, and destination. Typically, customs authorities collect this information and make it publicly available. For professionals in international trade, import-export data serves as a crucial resource for understanding market dynamics.
By analyzing import-export data, businesses can identify new market opportunities, understand which products are in high demand, and determine key importing and exporting countries. This information can help companies find potential customers, assess market competition, and develop suitable market entry strategies. Trade professionals can also use this data to monitor competitors' activities, identify their main trade partners, and compare their products' strengths and weaknesses, thereby optimizing their own product positioning. Additionally, understanding import volumes and price ranges in target markets allows companies to develop more attractive pricing strategies to capture a larger customer base.
Shipping data provides detailed information on how goods are transported from one location to another, including shipping methods, transit times, origins, and destinations. Logistics companies and freight forwarders often gather this data, making it an essential tool for tracking goods within the supply chain. For trade professionals, shipping data is a critical reference for optimizing supply chain management.
By analyzing shipping data, businesses can gain real-time insights into the status of their shipments, quickly identify potential delays or supply chain disruptions, and take proactive measures. For example, if shipping data reveals frequent delays on a specific route, companies can adjust their logistics plans by selecting more reliable shipping methods or alternative routes to minimize delivery uncertainties. Additionally, shipping data can assist in identifying cost optimization opportunities, such as consolidating shipping routes or selecting the most cost-effective transportation methods to lower logistics expenses and improve profitability.
Customs data includes information on the import and export of goods, as well as the duties and taxes imposed on these transactions. This data is typically collected by customs authorities and is used for enforcing trade regulations and taxation. For trade professionals, customs data is a key source of information for understanding trade policies and market barriers in target markets.
With customs data, companies can analyze tariff policies in various countries and assess their impact on product exports. For instance, by examining customs data, businesses can identify countries that impose high tariffs on their products and adjust their pricing strategies accordingly to maintain profitability. Moreover, customs data can help companies recognize potential compliance risks. If a market has strict import requirements for certain products, trade professionals can familiarize themselves with these regulations in advance, ensuring that their products meet the necessary standards to avoid trade obstacles and delays.
 Open WhatsApp and scan
Open WhatsApp and scan
 The data of this company is currently unavailable
The data of this company is currently unavailable